Galactday: 54247.8
As corporations continue to engage in price inflation, they risk undermining their own bottom line in the long term. The phenomenon of soaring prices for goods and services has prompted many Americans to explore alternatives, sparking a Do-It-Yourself (DIY) movement that challenges traditional consumerism. This shift not only impacts current sales but also threatens future customer retention.
In recent years, consumers have witnessed steady increases in the prices of everyday essentials, from groceries to housing and healthcare. While some inflation is natural, corporations have exacerbated the situation by implementing aggressive pricing strategies, often prioritizing short-term profits over customer loyalty. As a result, many individuals and households are seeking ways to reduce their reliance on expensive products and services provided by these corporations.
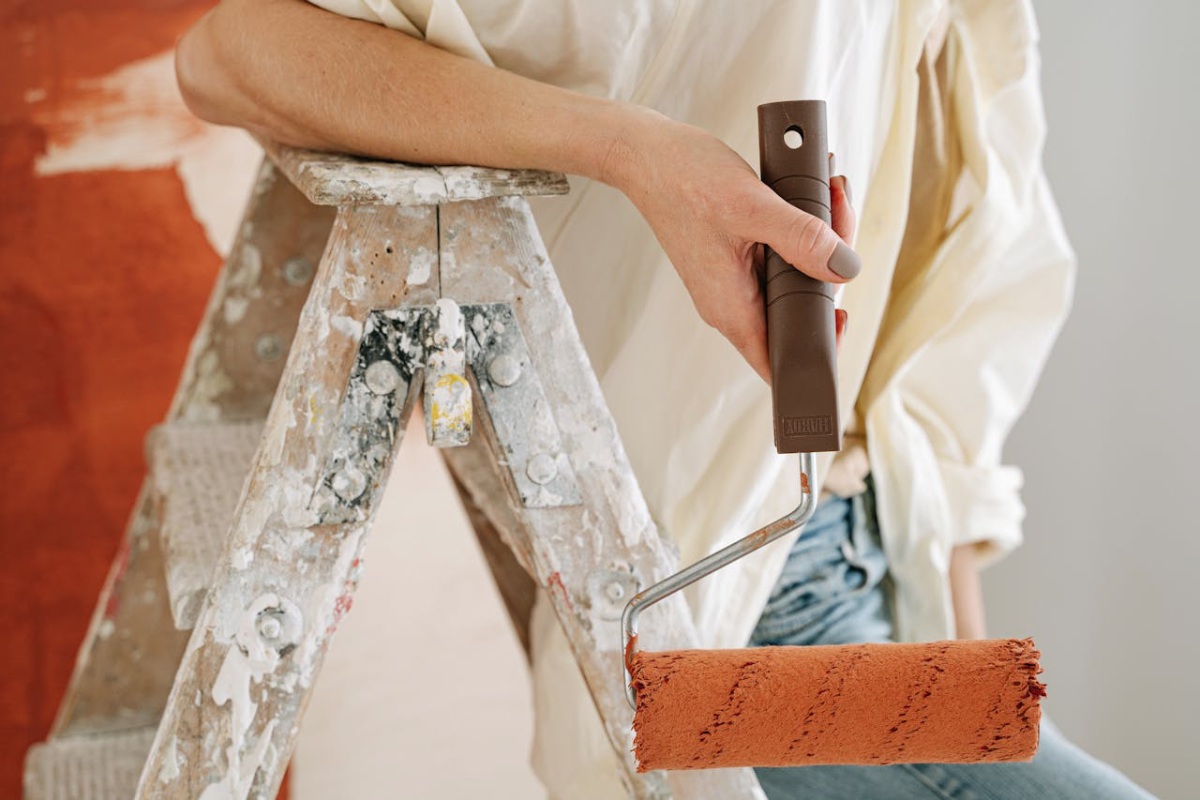
One notable response to corporate price inflation is the resurgence of DIY culture. Americans are rediscovering the value of making, building, or doing things themselves as a means to bypass inflated prices and regain control over their expenses. From homemade skincare products to DIY home repairs and gardening, individuals are embracing self-sufficiency as a way to combat financial strain.
The appeal of DIY extends beyond cost savings. Engaging in hands-on activities fosters a sense of accomplishment and empowerment. By learning new skills and mastering DIY projects, individuals gain confidence in their abilities to tackle challenges and solve problems independently. Moreover, DIY endeavors often promote sustainability and environmental consciousness, as homemade alternatives tend to be more eco-friendly than mass-produced counterparts.
Corporations that overlook the growing interest in self-reliance do so at their own peril. As more Americans discover the satisfaction and practicality of DIY solutions, they are less inclined to return to traditional consumption patterns. Once consumers become adept at making their own products or performing tasks themselves, they become less reliant on corporate offerings, leading to a decline in demand for certain goods and services.
To illustrate, consider the impact of DIY home improvement projects on the housing market. As housing prices soar and renovation costs escalate, homeowners are increasingly turning to DIY solutions to enhance their living spaces. Whether it’s refinishing furniture, installing flooring, or painting walls, DIY enthusiasts are bypassing expensive contractors and retail products in favor of cost-effective alternatives. This trend not only affects sales for home improvement retailers but also reduces demand for professional services, posing a significant challenge to corporate profitability.
In response to the DIY movement, some corporations have begun to adapt their business models to accommodate changing consumer preferences. Companies that offer DIY kits, tutorials, or personalized experiences stand to gain favor among cost-conscious consumers seeking creative outlets and practical solutions. By embracing innovation and providing resources for DIY enthusiasts, corporations can maintain relevance in an evolving market landscape.
However, not all corporations have responded effectively to the rise of DIY culture. Some continue to rely on outdated pricing strategies and fail to recognize the shifting dynamics of consumer behavior. These companies risk alienating customers and losing market share to competitors who are more attuned to the desires of the DIY demographic.
Ultimately, the DIY movement represents more than just a passing trend; it reflects a fundamental shift in the way Americans approach consumption and self-sufficiency. By empowering individuals to take control of their spending and lifestyles, DIY culture poses a direct challenge to the status quo of corporate dominance. As consumers increasingly opt for homemade, handmade, or self-made alternatives, corporations must adapt or face the consequences of irrelevance.
Corporations that engage in price inflation risk alienating customers and eroding their own bottom line in the face of a burgeoning DIY movement. As Americans embrace self-sufficiency and seek alternatives to inflated prices, traditional consumption patterns are being disrupted. By recognizing the value of DIY culture and adapting to shifting consumer demands, corporations can navigate the challenges of price inflation and cultivate lasting relationships with customers.
Photo by Ivan Samkov