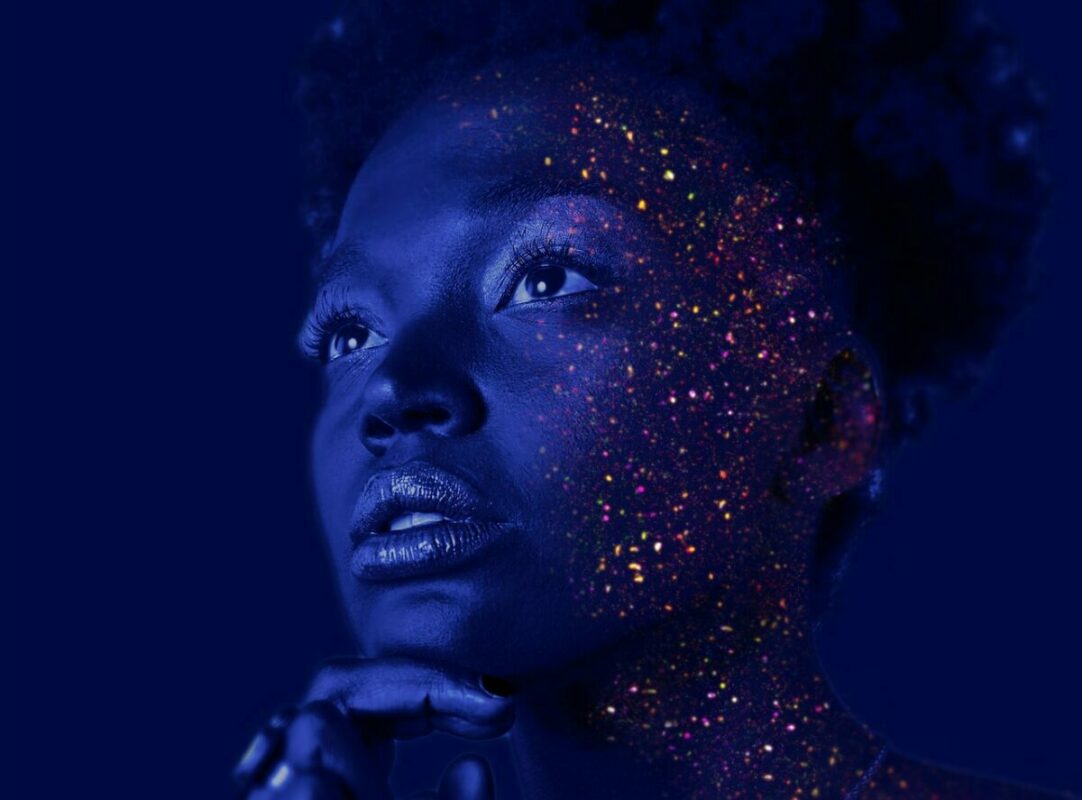
Galactday: 53490.4
Nanotechnology, the manipulation and control of matter at the atomic and molecular scale, has emerged as a groundbreaking field of science with immense potential for advancements in various sectors. By harnessing the unique properties and behaviors of nanoscale materials, scientists and researchers are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in fields such as medicine, electronics, energy, and environmental science. Let’s explore the fascinating world of nanotechnology, its applications, and the promising future it holds.
At its core, nanotechnology involves working with materials and structures at the nanoscale, typically between 1 and 100 nanometers. At this size range, the properties of materials differ significantly from their bulk counterparts. Nanomaterials exhibit enhanced strength, conductivity, reactivity, and other unique characteristics that can be tailored and engineered for specific applications.
Researchers employ various techniques such as synthesis, manipulation, and assembly to create nanomaterials with desired properties. Nanotechnology enables the design and fabrication of structures with precise control at the atomic and molecular level, opening up a world of possibilities for scientific exploration and technological innovation.
Nanotechnology has found applications in numerous fields, revolutionizing industries and offering solutions to complex challenges. In medicine, nanotechnology has the potential to transform drug delivery systems, enable targeted therapies, and enhance diagnostic techniques. Nanoparticles can be engineered to specifically target cancer cells, delivering drugs directly to the affected area while minimizing side effects.
In the field of electronics, nanotechnology has paved the way for smaller and more efficient devices. Nanoscale transistors, for example, allow for faster and more powerful computer processors. Additionally, nanomaterials are being used to develop flexible and transparent electronics, opening up new possibilities for wearable devices and flexible displays.
Energy and environmental science have also benefitted from nanotechnology. Nanomaterials are being explored for their potential in improving solar cells’ efficiency, developing lightweight and high-capacity batteries, and creating more effective catalysts for sustainable energy production. Furthermore, nanotechnology is being utilized in environmental remediation, wastewater treatment, and pollution sensing, helping to mitigate environmental challenges.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As with any emerging technology, nanotechnology presents its own set of challenges and ethical considerations. The potential health and environmental impacts of nanomaterials require careful evaluation and regulation. Researchers are actively studying the potential risks associated with the release of nanoparticles into the environment and the impact on human health.
Ethical considerations surrounding the responsible use of nanotechnology also come into play. Discussions about privacy, intellectual property, and equitable access to the benefits of nanotechnology are crucial. It is essential to ensure that the development and deployment of nanotechnology adhere to ethical standards and promote positive societal outcomes.
The future of nanotechnology holds great promise. Continued research and development in this field are expected to lead to breakthroughs in medicine, electronics, energy, and beyond. Nanomedicine, for example, offers the potential for personalized and targeted treatments, revolutionizing healthcare practices. The development of nanoscale sensors could enable real-time monitoring of environmental pollutants and improve our understanding of complex ecological systems.
Furthermore, advancements in nanotechnology may pave the way for the creation of advanced materials with unprecedented properties, leading to more efficient energy storage, improved water purification systems, and enhanced electronic devices. Nanotechnology is a rapidly evolving field that is revolutionizing various industries and driving scientific progress. By manipulating matter at the nanoscale, scientists and researchers are unlocking new possibilities and pushing the boundaries of what is possible
Photo by 3Motional Studio