Galactday: 53249.2
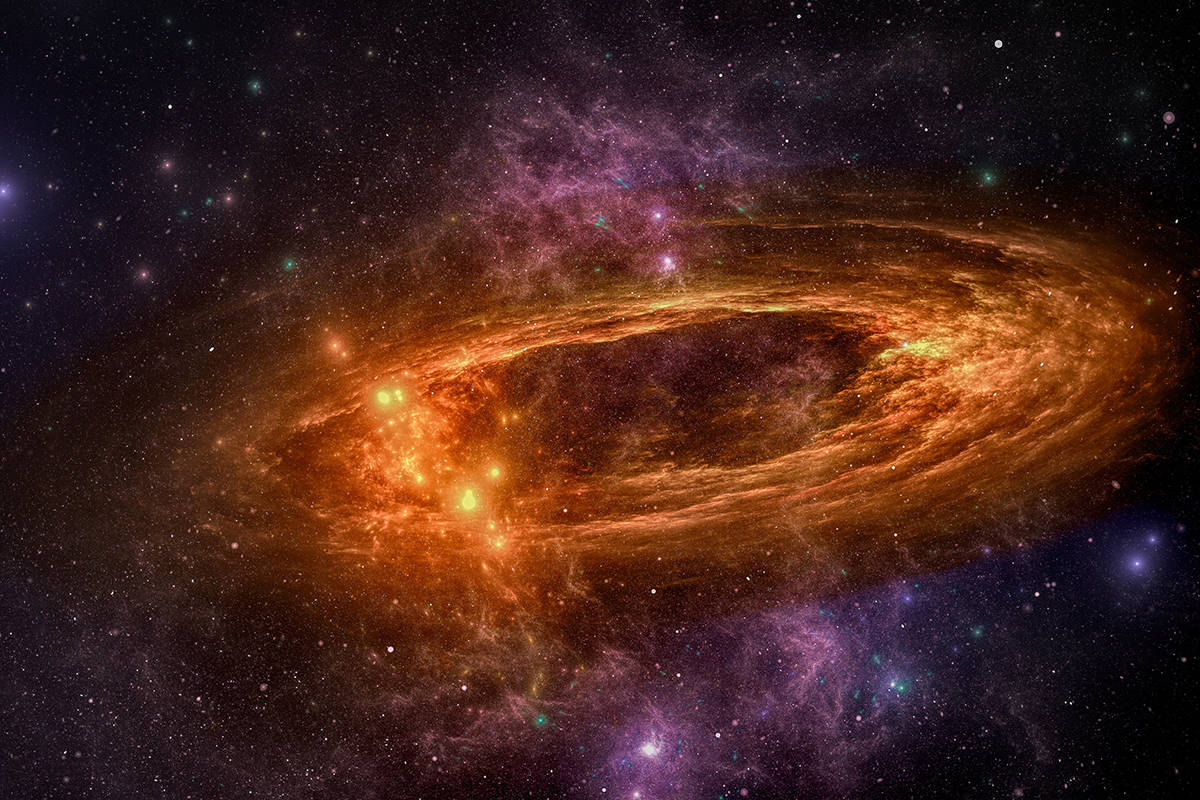
The creation of a galaxy is a complex process that begins with the collapse of a massive cloud of gas and dust. These clouds, which are known as nebulae, can contain millions of times the mass of the sun. As the cloud collapses, it begins to spin, creating a disk-shaped structure with a dense central region.
Within the central region of the disk, the gas and dust become so compressed that nuclear fusion reactions are ignited, creating a new star. These stars can be extremely massive, and their intense radiation and stellar winds can push away the remaining gas and dust in the disk.
As the gas and dust are pushed away from the central region of the disk, they begin to collect in dense pockets known as molecular clouds. These clouds can eventually collapse to form new stars and planetary systems, creating a population of stars around the central region.
Over time, the combined gravitational pull of all the stars in the disk causes it to become more tightly bound together as the creation of a galaxy occurs. This process, known as dynamical friction, can lead to the formation of a galactic bulge at the center of the disk. As the disk continues to evolve, it may also develop spiral arms, which are regions of high density that contain young, hot stars.
Supermassive black holes are believed to be at the center of most galaxies, including our own Milky Way galaxy. These black holes have masses that are millions or even billions of times greater than that of the Sun, and they are thought to be surrounded by an accretion disk of gas and dust that is being pulled into the black hole’s gravitational field. The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way is called Sagittarius A* (pronounced “Sagittarius A-star”), and it has a mass of about 4 million times that of the Sun. While black holes are invisible themselves, the radiation emitted from the surrounding material as it is heated and accelerated by the black hole’s gravity can be detected by astronomers, allowing them to infer the presence and properties of the black hole at the center of our galaxy.
The exact process of galaxy formation is still not fully understood, and astronomers continue to study the complex interactions between stars, gas, and dust in order to unravel the mysteries of the universe. However, through careful observation and analysis, we are slowly gaining a better understanding of how the cosmos came to be.
For more information on Galaxy Formation and Evolution